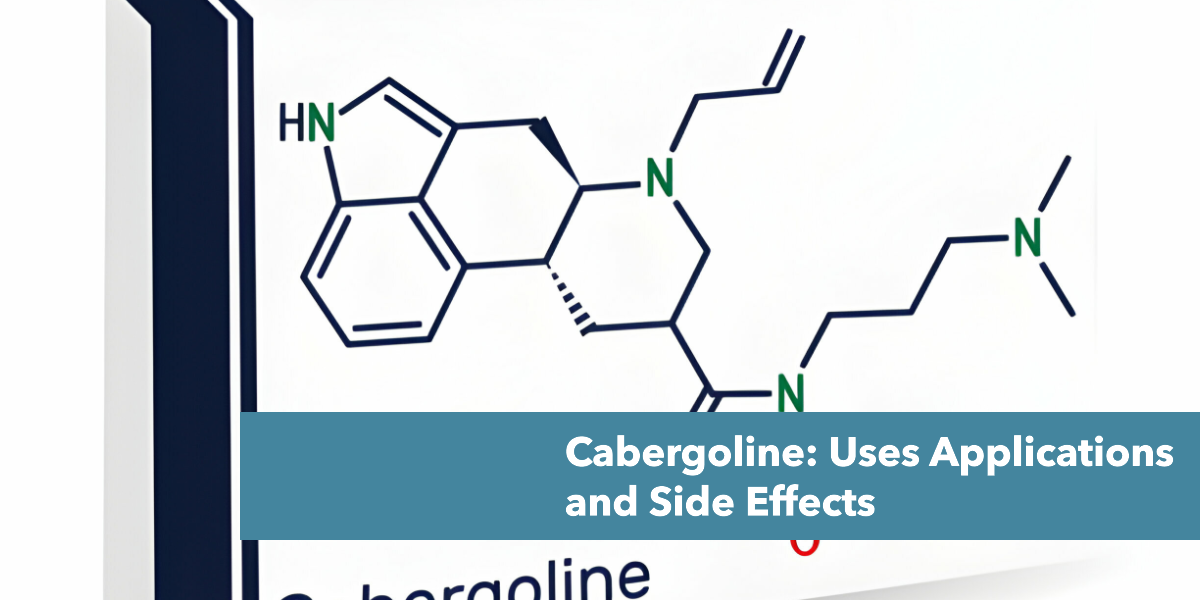
What is a Cabergoline?
Cabergoline is a dopaminergic medication most often used to treat high levels of the prolactin hormone in the body, a condition known as hyperprolactinemia. It is also sometimes used to treat Parkinson’s disease, prolactinomas, and acromegaly.
Cabergoline is a prescription-only ergot derivative and long-acting dopamine receptor agonist, often sold under the brand name Dostinex. When treating hyperprolactinemia, it works by blocking the release of prolactin from the pituitary gland. It is also used off-label to treat infertility.
How Does Cabergoline Work?
Cabergoline is a dopamine receptor agonist, which has a high specificity and affinity for the dopamine D2 receptor, although it also has an affinity for other receptors. Its mechanism of action involves binding to these receptors in the pituitary gland, which inhibits the release of prolactin. This reduces prolactin levels in the body, which in turn treats symptoms of hyperprolactinemia.
How to Use Cabergoline?
Cabergoline comes as an oral tablet which is usually taken twice a week, with or without food. The dosage depends on the condition being treated and should be followed as directed by a doctor. In the case of hyperprolactinemia, the starting dose is often 0.25mg, increased by 0.25mg every four weeks.
The medication should be stored at room temperature, away from moisture and light, and out of the reach of children.
Remember to speak to a doctor before taking any medication.
What are the Side Effects of Cabergoline?
Cabergoline has many potential side effects, although these are often mild and may go away during treatment. They include:
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Dizziness
- Tiredness
- Constipation
- Dry mouth
- Diarrhea
- Headache
- Increased libido
- Insomnia
- Hallucinations
- Irregular heartbeat
- Swelling of the face, arms, hands, or feet.
- Weight gain or loss.
- Chest pain or tightness.
- Difficulty breathing when lying down.
More severe side effects require immediate medical attention. These include:
- Allergic reactions, including swelling of the throat or tongue.
- Vision changes.
- Cough that doesn’t go away.
- Sudden changes in mood.
- Uncontrollable urges, including increased sexual urges and gambling.
- Painful periods.
- Breast pain.
- Decreased urination.
- Back or side pain.
- Lumps or pain in the stomach area.
- Difficulty concentrating.
Side effects may be more severe in those with certain health conditions, or when used to treat Parkinson’s disease or restless leg syndrome, as this often requires very high doses. In rare cases, it can cause heart valve problems, organ tissue scarring, and liver function abnormalities.
The medication’s label also warns of the potential for intense or unusual behaviors, including gambling, and for users to be aware of family members exhibiting these symptoms.
How Long For Cabergoline to Work?
Cabergoline’s effect on lowering prolactin levels can be seen in two ways:
Initial Impact: This is quite fast. Studies show a significant decrease in prolactin levels within 3 hours of taking Cabergoline.
Long-Term Effect: The medication has a long-lasting effect due to its slow elimination from the body. This extended action helps maintain lower prolactin levels over time.
However, the degree of prolactin reduction and the time it takes to see its full effects depend on several factors, including:
Dosage: The amount of Cabergoline prescribed will influence how much prolactin levels are lowered.
Individual factors: People metabolize medication differently, so it might take some time to find the optimal dose for you.
Underlying condition: The severity of your prolactin-related condition can affect how long it takes to see full benefits.
Here’s the key takeaway: While Cabergoline has a rapid initial impact, it can take weeks or even months to see its full effect on prolactin levels and experience the complete benefits for your specific condition.
Remember: It’s crucial to discuss your progress with your doctor during regular checkups. They can monitor your prolactin levels and adjust the dosage if needed to achieve the desired outcome.
What are the Possible Uses of the Cabergoline In Pakistan?
Treatment of prolactinomas: These are tumors on the pituitary gland that cause it to produce too much prolactin hormone. Cabergoline helps shrink the tumor and lower prolactin levels.
Lowering prolactin levels for fertility: In women with infertility or menstrual irregularities caused by high prolactin, Cabergoline can help regulate their hormones and improve fertility.
What are the Regulations for Cabergoline Use in Pakistan?
The regulations for Cabergoline use in Pakistan are as followed below.
Cabergoline is a registered pharmaceutical drug in Pakistan that is approved for use. The Drug Regulatory Authority of Pakistan (DRAP) maintains a registry of applications for pharmaceutical drugs.
The recommended therapeutic dose of Cabergoline in Pakistan is 1 mg (two 0.5 mg tablets) as a single dose, typically administered within the first day post-partum for the purpose of lactation inhibition.
Prescribing patterns for Cabergoline in Pakistan show that it is mainly used to inhibit lactation in cases of stillbirth, abortion, and neonatal death. However, it is also sometimes prescribed for mothers with live babies who have other medical conditions.
The regulations require that Cabergoline be prescribed appropriately in terms of timing (within 27 hours of delivery/abortion). Around 74% of prescriptions in Pakistan were found to be within these guidelines.
Cabergoline is not a controlled substance in Pakistan and is not subject to the Controlled Substances Act, unlike in some other countries.
What are the Warning and Precautions of the Cabergoline?
Warnings
Cabergoline has several associated warnings. These include:
It may cause heart valve problems, which can be checked with an echocardiogram. It should not be used by those with heart valve disorders, and symptoms of heart issues such as chest pain and shortness of breath should be reported to a doctor immediately.
It may cause organ tissue scarring, a condition known as fibrosis. Tell your doctor if you have a history of this.
It is not suitable for those who are pregnant, breastfeeding, or under 18 years old.
Avoid if you have uncontrolled high blood pressure, or a history of pregnancy-induced high blood pressure (eclampsia or preeclampsia).
Tell your doctor if you have a mental health problem or a history of psychotic disorders.
Cabergoline may interact with other medications, vitamins, or herbs, including antipsychotic drugs, anti-nausea drugs, and lorcaserin, so make sure your doctor knows all the medicines you take.
It may cause sudden sleep onset, so take extra care when driving or operating machinery.
There have been reports of unusual behavior, including increased sexual urges and gambling. Family members should be made aware of this side effect, so they can contact a doctor if the patient is unable to recognize the problem.
Precautions
Some precautions to take when using cabergoline include:
Getting up slowly from a sitting or lying position, to avoid dizziness.
Regularly attending check-ups with a doctor, who can perform tests to monitor the function of your heart.
Storing the medication carefully, out of reach of children.
Not flushing the medication down the toilet or pouring it down a drain, following disposal guidance instead.
How Does Cabergoline Interact with Other Medicines?
Cabergoline has many potential drug interactions and should not be used with certain medications.
Drugs which should be avoided when taking cabergoline include:
Antipsychotics such as haloperidol, chlorpromazine, and clozapine.
Anti-nausea drugs like metoclopramide and promethazine.
Beta-adrenergic blockers for example, atenolol, propranolol, and sotalol and decongestants such as phenylephrine and pseudoephedrine.
Ergot alkaloids, including ergotamine and dihydroergotamine.
Macrolide antibiotics, such as clarithromycin.
Lorcaserin.
Other medications to be aware of when taking cabergoline include antipsychotic drugs, anti-nausea drugs, and naratriptan—the combination could increase toxicity or cause additive vasospasm. It also has several interactions with blood pressure medications, and may interact with painkillers, including codeine and tramadol.
Cabergoline is also known to interact with grapefruit and St John’s Wort, which may decrease its serum concentration.
Check with a doctor or pharmacist before taking any new medication to ensure it is safe to do so alongside cabergoline.
What happens if I miss a dose of Cabergoline?
If you miss a dose of cabergoline, take it as soon as you remember, unless it’s nearly time for your next dose. In this case, skip the missed dose and continue with your regular schedule, avoiding taking two doses at once.
What happens if I overdose on Cabergoline?
If you overdose on Cabergoline, you may experience symptoms such as stuffy nose, hallucinations, fainting, and other serious effects. An overdose of Cabergoline can lead to severe consequences and requires immediate medical attention. Symptoms of overdose may include stuffy nose, hallucinations, or fainting.
What are the Alternatives of the Cabergoline That are Used in Pakistan?
We understand you might be looking for treatment options for hyperprolactinemia in Pakistan. Cabergoline is one medication used for this condition, but there are other alternatives available.
Bromocriptine: This medication works similarly to Cabergoline and is often the first-line treatment for hyperprolactinemia. It can help normalize prolactin levels and restore fertility.
Quinagolide: Another option is Quinagolide, which works in a similar way to Cabergoline to lower prolactin levels.
Lisuride: This is a less common medication, but it can be an alternative if other options are not well-tolerated or effective for you.
Surgery: In some cases, if medications aren’t successful, surgery may be an option. This surgery removes the pituitary tumor causing the prolactin overproduction.
Other medications: Depending on the underlying cause of your hyperprolactinemia, your doctor might consider other medications such as estrogen-lowering drugs or gonadotropin-releasing hormone agonists.
Wichtig (Important): It’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the most suitable treatment for you. They can consider your specific condition and medical history and offer personalized advice on the available alternatives to Cabergoline in Pakistan.
How Successful is Cabergoline Tablet in Pakistan?
The Success of the Cabergoline Tablet in Pakistan based on the some studies.
Studies have shown cabergoline to be more effective than bromocriptine in normalizing prolactin levels in hyperprolactinemic patients in Pakistan. The percentage of success in attaining normal prolactin levels with cabergoline was higher compared to bromocriptine.